Collagen Treatments
Collagen is one of the most important substances in your body. It’s a glue that helps the body maintain its shape and structure by binding tissues and cells. With age, natural collagen production begins to slow, and cell structures weaken. Skin becomes thinner and sags while ligaments lose their elasticity, joints get stiffer, and much more. In this article, we’ll dig deeper into what collagen is, how it works, and methods to replenish it in your body regardless of how old you are.
What Is Collagen?
Collagen is a protein found in muscles, tendons, skin, ligaments, and bones. It makes up about 30% to 40% of proteins in the human body.
Naturally, collagen occurs exclusively in animals. It’s part of the connective tissue, which is responsible for the firmness of different structures in the body. While it is vital for the overall integrity of your body, protein is especially important for the skin’s elasticity.
At least 16 types of collagen exist. However, the first three types account for about 80% to 90% of it.
- Type I –accounts for about 90% of all collagen in your body. It helps keep cells and tissues together in the skin, tendons, bones, teeth, and fibrous cartilage.
- Type II –is found in elastic cartilage and cushions joints.
- Type III –supports the integrity and structure of organs, arteries, and muscles.
How Does Collagen Affect Your Skin?
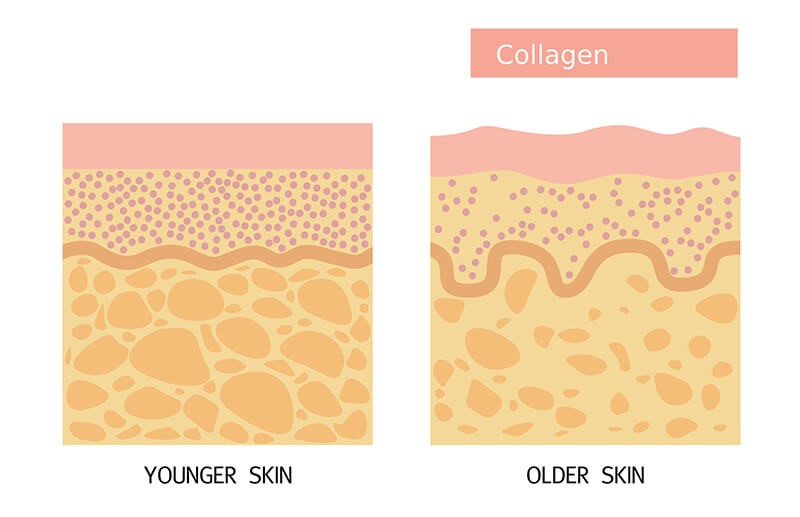
Collagen comprises 70% of the dry skin mass. It strengthens your skin and benefits its elasticity and hydration. Collagen fibers create the infrastructure for elastin and hyaluronic acid, which are responsible for skin’s elasticity and hydration.
As you age, your body starts producing less collagen. The skin becomes thinner, drier, and less elastic. The loss of collagen leads to wrinkle formation.
Your body begins to lose collagen when you turn 30. The effects become noticeable after several years. Even though this is a natural process, it’s possible to speed it up with UV exposure, pollution, bad habits, and poor diet choices.
As the amount of collagen decreases, other parts of your body suffer as well:
- Bones –become weaker and more fragile
- Joints –cartilage wears out, making it tough to stay active
- Muscles –function decreases affecting mobility and balance
While it’s possible to accelerate collagen loss, it’s also possible to slow it down. We’ll talk about this a little later.
